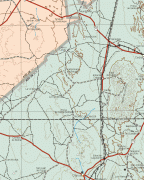
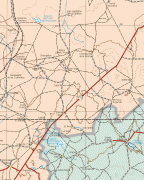
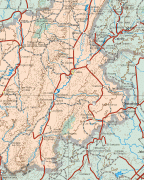
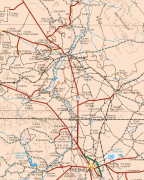
Zacatecas (Estado de Zacatecas)
 |
 |
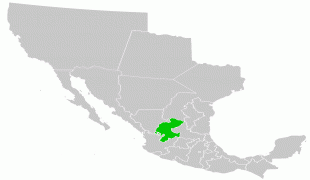
Zacatecas is located in North-Central Mexico. It is bordered by the states of Durango to the northwest, Coahuila to the north, Nayarit to the west, San Luis Potosí and Nuevo León to the east, and Jalisco, Guanajuato and Aguascalientes to the south. The state is best known for its rich deposits of silver and other minerals, its colonial architecture and its importance during the Mexican Revolution. Its main economic activities are mining, agriculture and tourism.
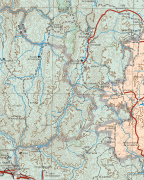
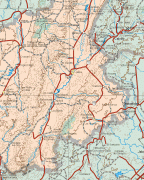
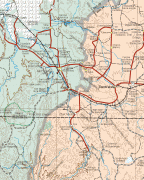
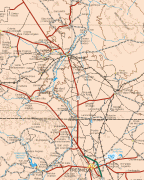
Zacatecas is located in the center-north of Mexico, and covers an area of 75,284 km2, the tenth-largest state in the country. It borders the states of Nayarit, Jalisco, Aguascalientes, San Luis Potosí, Coahuila and Durango and is divided into 58 municipalities and 4,882 towns, cities and other communities.
The state has an average altitude of 2230 meters above sea level, with the capital at 2,496 masl. The state has three main geographical regions, the Sierra Madre Occidental in the west, the Mexican Plateau and the Sierra Madre Oriental. Most of it is in the Sierra Madre Occidental with highly rugged peaks of over 2,500 meters above sea level. The mountains of the southeast and northeast are lower but there are large valleys such as the Juchipila and Tlaltenango. Most of the territory has only small mesas and other areas of flat land. In the center of the state there is a small mountain chain called the Sierra de Fresnillo, from which much of the state's mineral wealth comes. In the extreme northwest there is another important mountain chain called the Sierra de Sombrerete, marked by a mountain called Sombreretillo, which is an important source of mineral wealth. Near this chain is another called the Sierra de Órganos.
No major rivers run through the state and most of the waterways run only during the rainy season. The state is part of two water basins. The southeast of the state belongs to the Lerma River basin, which eventually empties in the Pacific Ocean. Rivers belonging to this basin include the San Pedro, Juchipila, Jerez and Tlaltenango. The other basin is smaller and endorheic, and does not empty into any ocean. The state has eighty dams with a total capacity of 595,337 million cubic meters. The largest of these are the Leobardo Reynoso in Fresnillo, Miguel Aleman in Tepechitlan and El Chique in Tabasco. Much of the state's water is underground divided into twenty hydraulic zones. These are accessed by over 5,800 wells, mostly for agricultural use.
Most of the territory has a cool, dry climate, although areas in the south have more moisture, with most rain falling between June and September. The driest and coldest areas are in the northeast, known as the Salado because of its saltwater lakes. 75% of the state is arid or semi-arid. 14% is arable and 79% is suitable for the grazing of livestock.
The average annual temperature is 16C with most of the state being temperate. The coldest months are from November to January, with frost not uncommon. The warmest month is June. The state gets an average rainfall of 400mm per year mostly in the summer, with the warmest and wettest part of the state is along the Sierra Madre Occidental.
Ecosystems vary depending on relief, soil and temperature, leading to a wide variety of vegetation, including forests, scrub and grasslands. Arid areas are dominated by various species of cactus. In the far south there are deciduous trees that lose their leaves in winter and spring. Statewide the most common trees are mesquite, ironwood and palo verde (Parkinsonia). In the highest altitude, near the Jalisco border, there are mixed forests of pine and holm oak, with the latter dominating along the border with Durango and some along the border with San Luis Potosí. One interesting tree that occurs in Zacatecas is the elephant tree (Bursera microphylla). In the sierras there are many wild boar, white-tailed deer and hares; in the valleys and plains it is common to find coyote, badgers, quails and ducks. The extreme northern part of the state is the southern fringe of the Chihuahuan Desert and as such is rich and diverse in biology. This desert is home to a large amount of cacti and is one of the most ecologically diverse deserts on earth.
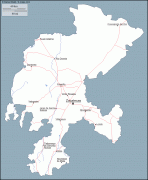
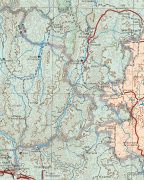
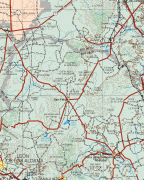
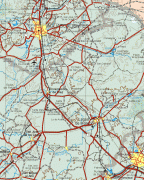
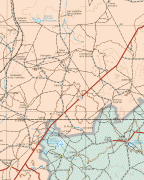
Map - Zacatecas (Estado de Zacatecas)
Map
Country - Mexico
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| MXV | Mexican Unidad de Inversion | 2 | |
| MXN | Mexican peso | $ | 2 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| ES | Spanish language |